Although there are inconsistencies to the many and varied claims of the health benefits of tea – Green Tea in particular – one benefit that all can agree on is that tea contains high levels of anti-oxidants. Anti-oxidants offer protection against free radicals, but what are they and how do they interact to keep us healthy?
Meet the Players
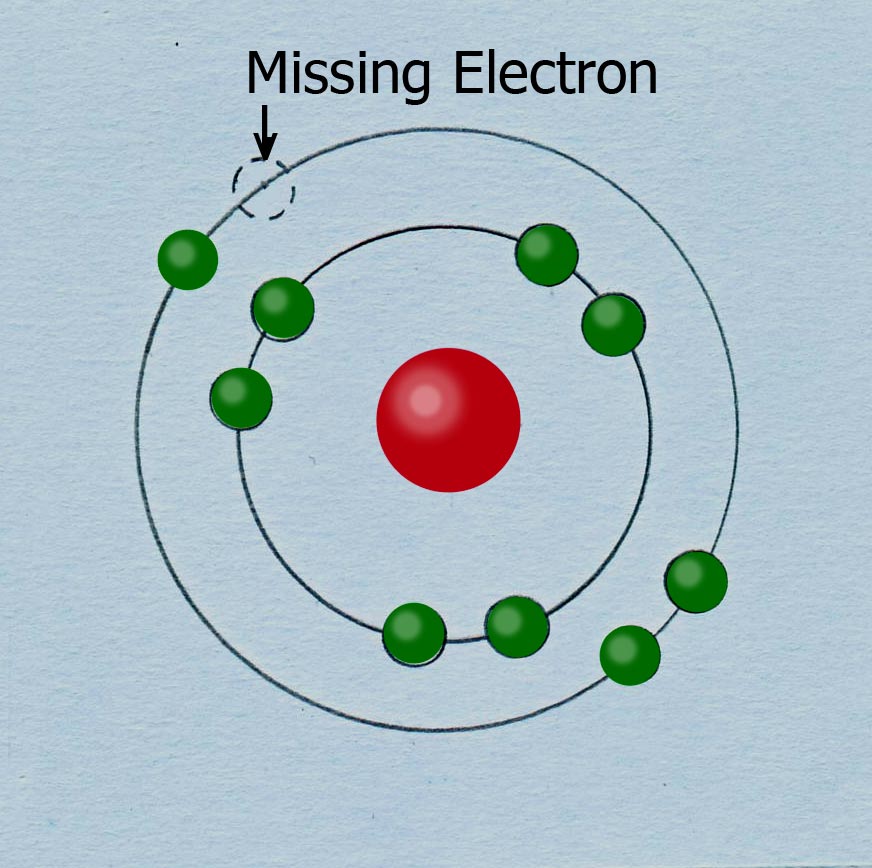
The Enemy: A free radical is an atom or molecule that has an unpaired electron in one of its orbits. An atom consists of a nucleus around which pairs of negatively-charged electrons circulate in one or more orbits. If one of these electrons should be lost, either by aging, illness, or environmental factors, the atom becomes extremely unstable. This is what is called a free radical. Such a free radical is then likely to link up with any other atom floating around that has an electron to spare, creating a potentially unhealthy or dangerous union – a characteristic it shares with political radicals who may also form undesirable associations.

The Hero: Anti-oxidants to the rescue! An anti-oxidant is a molecule that also has an electron to spare, but when it hooks up with a free radical it forms a compound that is benign. So if we drink lots of green tea we will have lots of anti-oxidants with their extra electrons, and hopefully these will be able to attach themselves to our free radicals before those radicals form liaisons with less-desirable company.
Of course, the real health benefit of green tea is this: if you are drinking green tea you are not drinking rum-and-coke, a sixth cup of coffee, or a jug of chocolate milk.